Multimedia Gallery
- Navigation Methods: Satellite Navigation
This computer, located in the Alabama’s navigation center, processed the data derived from the gyroscopes and accelerometers.
This is a model of a platform that is isolated from the movements of the ship, allowing those movements to be measured.
The Motorola LGT 1000 was used for better accuracy by scientists.
In the 1990s, the NIST-7 was the most accurate clock in the country and helped keep the GPS clocks synchronized.
A rubidium clock like this was tested on the NTS-2 satellite to see if clocks could keep accurate time in space.
The NTS-2 Development Team at the Naval Research Laboratory.
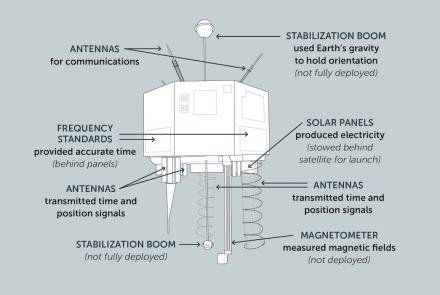
This illustration shows the important components of the NTS-2 satellite.
Engineers discussing the Global Positioning System.
The PLGR was smaller and lighter than the older Manpack GPS receiver.